A new format for this week’s COVID-19 update: as well as summarising our regular fortnightly report for SAGE (including research highlights) we have also published a summary of the Data & Connectivity (and the full report) as part of our involvement in the National Core Studies.
Highlights:
- There have been eight additions to active COVID-19 research taking place (total now over 190) with most new projects enabled by NHS Digital data
- This includes daily access to positive COVID-19 test results, to allow increased recruitment to PRINCIPLE trial
- There has been a significant improvement in dataset discoverability (via the Health Data Research Innovation Gateway) in the last 2 weeks including Pillar 1 & 2 testing data with technical metadata
- Research highlights include the increasing focus on geography and location in analysis of COVID-19 (including the use of data from Facebook for Good to track when people have shared their locations); mental health also continues to be focus of many research studies, one of which looked at the link between anxiety and COVID-19 transmission rates
- Of course, the news that Pfizer and BioNTech have data that show that their vaccine is 90% effective in preventing COVID-19 made international news
Read our latest report to SAGE
Making UK-wide health and administrative data available for linkage and accessible to catalyse COVID-19 research
National Core Studies – Data & Connectivity – Sprint One Report
Established in October 2020, the National Core Studies programme consists of six studies, including the cross-cutting Data and Connectivity component, led by HDR UK and ONS. Data and Connectivity accelerates the answering of key research questions about COVID-19 by enabling streamlined access to core datasets, linkage and analysis.
The Data and Connectivity Programme runs as a series of five consecutive one-month “sprints”, starting in October 2020; and is already having an impact, enabling the UK to use health data and research to inform both our near and long-term responses to COVID-19.
Summary of Sprint One
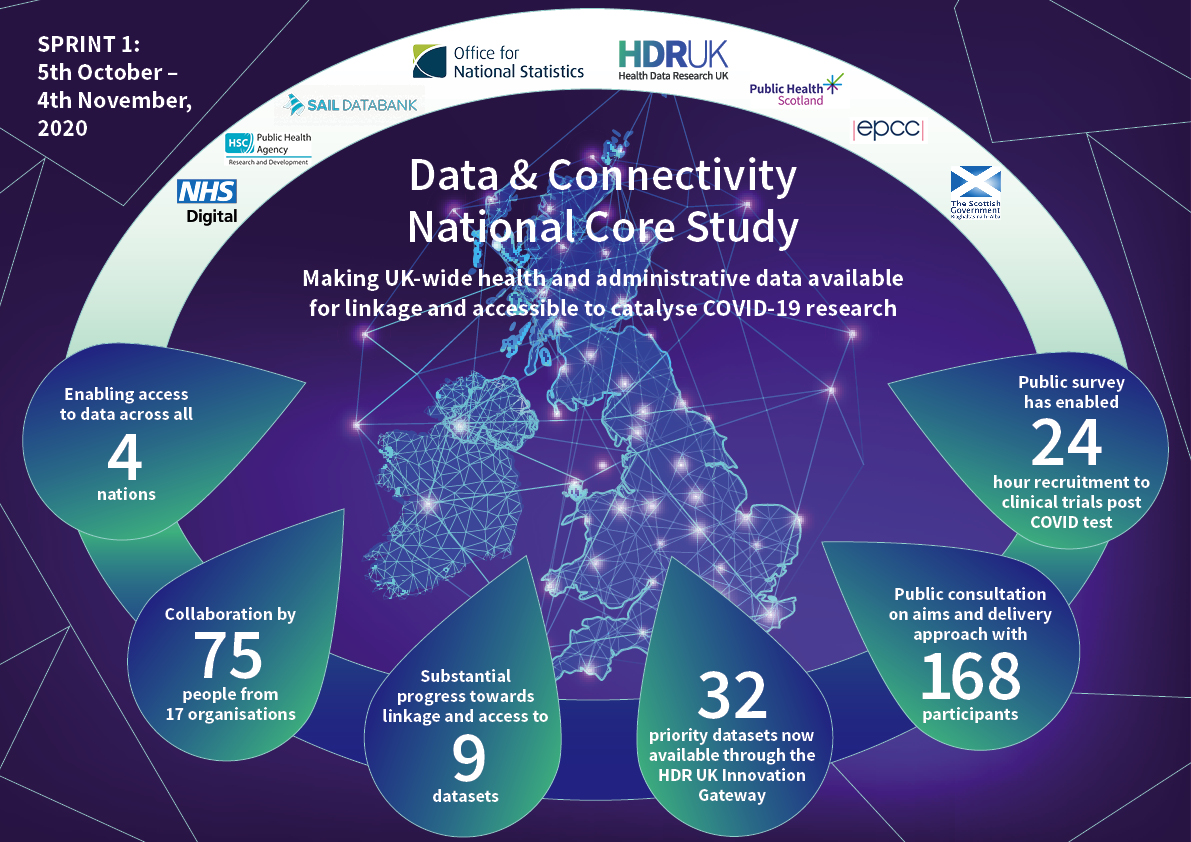
These outcomes demonstrate the substantial impact HDR UK has achieved in just four weeks by being able to bring together our partners and leading a crucial workstream at pace that has delivered results that will have a tangible impact on people’s lives in the UK.
Sprint Two will continue this progress, including making further datasets available in the HDR UK Innovation Gateway and the UK’s trusted research environments to make this vital data available for analysis, ethically and safely, to accelerate COVID-19 research.
Summary of our latest report to SAGE:
Pfizer and BioNTech announce positive efficacy results for COVID-19 vaccine
The clinical trial into a vaccine for COVID-19 being run by Pfizer and BioNTech has announced that the vaccine candidate being used has been found to be more than 90% effective in preventing COVID-19 in participants without evidence of prior infection. They have reported that data on the safety of this potential vaccine is needed before they are able to apply for the FDA Emergency Use Authorisation (which they intend to do). This data is estimated to be available by the third week of November. This is an important first step towards an effective vaccine for COVID-19 and we eagerly await further updates.
Coronavirus Infection Survey shows larger portion of asymptomatic infections in second wave
Results from the ONS Coronavirus Infection Survey show changes in infection within communities from April 2020 and September 2020. The percentage of people testing positive for COVID-19 showed a decrease from April to June, with lower levels continuing into the summer. However, there was an increase in percentages of people testing positive towards the end of August and September. The survey showed that having a patient-facing role and those working outside of your home were groups which experienced higher risk of infection which has not continued into the second period of increased positive test. It also reported that a substantial proportion of infections (53-70%) during August and September were people who did not report symptoms.
COVID-19 symptom study app data used to detect hotspots
By performing modelling on longitudinal, self-reported data from users of the Symptom Study App and a predictive model provided by the Department of Health, researchers were able to estimate number of cases, prevalence and effective reproduction numbers for different areas around England. Using the data provided by more than 2.6 million app users, researchers were able to estimate and highlight regions before they were subject to local government lockdowns. This demonstrates the important role self-reported data in research being undertaken into COVID-19.
You can also read our case study on COVID-19 geographical hotspots here
Daily human mobility data used to track movements between communities during lockdown
Data from Facebook for Good has been used to track the movement of communities during both the first national lockdown and locally-targeted interventions. This real-time data is crucial as it shows that people did not reorganise the same way during the first lockdown as they did when they were faced with local interventions. The transport networks people chose to take were largely the same, but with measurable mobility effects decreased. This type of data shows distribution of people change across the UK, which allows researchers to asses which geographic areas may need targeted interventions.
Data in England shows declining prevalence of COVID-19 antibody positivity
A study of 365,000 adults tested for antibodies, which ran across three months, shows a decline in the antibody prevalence across this time. There was a decline of 26.5% over the three months of the study. Those in the youngest age group (18-24) showed the highest prevalence of a positive result and smallest overall decline in positivity. The opposite showed for oldest age group (75+).
Large mental healthcare database is used to assess causes of death during first wave of COVID-19 pandemic in comparison to 2015-2019
Researchers have used a large mental healthcare database liked to death registrations to assess and describe the numbers of deaths within underlying-causes-of-death groups for the period of March to June in 2020, and compared these with the same time periods in 2015-2019. Of the 1109 excess deaths during this time period in 2020, 63.85% of these were deaths relating to COVID-19. The remaining 36.15% of these excess deaths are attributed to unnatural/unexplained deaths and by deaths recorded due to neurodegenerative conditions. It is likely that some of these deaths were a result of increased suicide rates during lockdown.
US Study determines that survivors of COVID-19 may be at increased risk of psychiatric sequelae and a psychiatric diagnosis may be an independent risk factor for COVID-19
The study used a global federated network which captures anonymised data from electronic health records totalling 69.8 million patients. They used this data to measure the incidence of and hazard rations for psychiatric disorders including dementia and insomnia, during the first 14-90 days after COVID-19 diagnosis. The study found that COVID-19 was more likely to increase incidences of a first psychiatric diagnosis than six other health events (such as influenza or fracture of a large bone). It also determined that a psychiatric diagnosis within the previous year was associated with a higher incidence of COVID-19 diagnosis.
Linked cases of infection identified using data collected from two wards at Cambridge University Hospitals
This method, developed as part of COG-UK, provides rapid analysis of data from clinical or other outbreak settings. The method combines knowledge of infection dynamics, data around how people have been moving around, and new approaches to genome sequencing to assess whether or not infection cases are consistent with what linkage via transmission. Researchers compared patterns of linkage between one designated COVID-19 ward and non-COVID-19 wards.
RECOVERY trial Data Monitoring Committee concludes that recruitment of eligible patients to all arms of the trail should continue
This committee reviewed the safety and efficacy data available for the 15,545 patients randomised. The committee concluded that there was no reason to modify the protocol or intake into the study and that recruitment should continue into all arms of the trial.
In addition to this, Aspirin has been added to the list of possible treatments by the RECOVERY trial, taking place across 176 hospital sites across the UK. This is due to patients with COVID-19 being more susceptible to blood clots forming in the blood vessels, which aspirin (an antiplatelet) has the potential to reduce the chance of.
Study recommends clinical trial looking into whether hydroxychloroquine is effective as a preventative treatment to COVID-19
Although studies found no evidence of reduced mortality when treating patients with COVID-19 with hydroxychloroquine, it has been shown to exhibit signs that it should be investigated as a preventative treatment which would reduce the number of people falling ill with COVID-19. The below study used national primary care data and linked death registrations in the OpenSAFELY platform (covering 40% of the general population of England) to conduct an observational study which found that there was no evidence of benefit or harm between people with the same health conditions prescribed hydroxychloroquine with regards to COVID-19. Therefore, the study recommends a clinical trial to assess the viability of this drug as a preventative measure to transmissions of COVID-19.



